Table of fines
Penalty Catalog for Distance Violations, As of: März 2025
At less than 80 km/h
| Distance Violation | Fine | Penalty Points | Suspension | File objection? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| without endangerment | 25 € | - | - | rather not |
| with endangerment | 30 € | - | - | rather not |
| with property damage | 35 € | - | - | rather not |
From 80 km/h to 100 km/h
| Distance less than | Fine | Penalty Points | Suspension | File objection? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5/10 of halved km/h value | 75 € | 1 | - | check here |
| 4/10 of halved km/h value | 100 € | 1 | - | check here |
| 3/10 of halved km/h value | 160 € | 1 | - | check here |
| 2/10 of halved km/h value | 240 € | 1 | - | check here |
| 1/10 of halved km/h value | 320 € | 1 | - | check here |
From 100 km/h to 130 km/h
| Distance less than | Fine | Penalty Points | Suspension | File objection? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5/10 of halved km/h value | 75 € | 1 | - | check here |
| 4/10 of halved km/h value | 100 € | 1 | - | check here |
| 3/10 of halved km/h value | 160 € | 2 | 1 month | check here |
| 2/10 of halved km/h value | 240 € | 2 | 2 months | check here |
| 1/10 of halved km/h value | 320 € | 2 | 3 months | check here |
At more than 130 km/h
| Distance less than | Fine | Penalty Points | Suspension | File objection? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5/10 of halved km/h value | 100 € | 1 | - | check here |
| 4/10 of halved km/h value | 180 € | 1 | - | check here |
| 3/10 of halved km/h value | 240 € | 2 | 1 month | check here |
| 2/10 of halved km/h value | 320 € | 2 | 2 months | check here |
| 1/10 of halved km/h value | 400 € | 2 | 3 months | check here |
Distance Violations as a Cause of Accidents
In Germany, violations of the minimum distance are among the common causes of accidents. While for many years, the number of accidents caused by distance violations lagged behind those caused by speeding violations, in 2014, it surpassed the declining trend of accidents caused by excessive speeding.
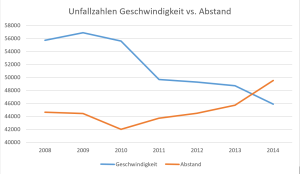
Due to the relatively high number of accidents caused by distance violations, they are strictly enforced. Similar to speeding violations, the penalties are based on the potential risk to the safety of both the driver and other road users.
The Right Distance
General Regulations
To travel safely on the road, it is recommended to maintain the correct safety distances. These distances are especially important for:
- Distances to vehicles in front on the same lane
- Lateral distances to parallel-moving vehicles and road users in the same direction
- Lateral distances to oncoming vehicles on roads without physical lane separation (guardrails, green strips)
- Lateral distance to the edge of the road.
Regarding accident statistics, the distance between vehicles traveling in the same lane plays by far the most significant role. Therefore, authorities focus on monitoring compliance with minimum distances in the direction of travel and penalizing violations.
According to the Road Traffic Regulations, the distance to a vehicle in front must generally be large enough to allow the following vehicle to come to a safe stop even in the event of sudden braking by the leading vehicle (cf. §4 para. 1, sentence 1 StVO).
Rule of Thumb for Minimum Distance
In the Direction of Travel
- Inside cities:
Distance covered in one second
Speedometer reading / 3.6 (approximately 15 meters at 50 km/h or 3 car lengths) - Outside cities:
Distance covered in 2 seconds
Rule of thumb: “half the speedometer”:
Divide the speed in kilometers per hour by 2
Result in meters -> Minimum distance
Lateral Distance
- Single-track vehicles (bicycle, motorcycle): minimum 1.5 meters
Rule of thumb: The door should be able to open without the rider falling off - Two-track vehicles (cars, trucks): minimum 1 meter
- Waiting school and shuttle buses: at least 2 meters
- The higher the speed, the greater the distance should be
Situation-Dependent Adjustment
The safety distance must be adjusted to weather conditions, visibility, and load. Therefore, the correct distance can be much larger than the measurements indicated in the rule of thumb.
The Distance Violation
The traffic situation, with its natural variations, can lead to reductions in distance without the driver’s fault. Not every insufficient distance is considered a distance violation.
What Constitutes a Distance Violation?
The Higher Regional Court of Hamm established in its decision of July 9, 2013, Ref.: 1 RBs 71/13, two criteria that must both be met for a distance violation to be present:
- Criterion 1: Duration
- Distance violation lasting at least 3 seconds, or when the minimum distance is not maintained over a distance of at least 140 meters
- The 140 m limit applies regardless of speed: If you drive faster, you consciously take a higher risk and must therefore correct your distance more quickly to avoid being penalized
- In other cases, there is a so-called momentary lapse. If the violation is only brief, it cannot be penalized. Therefore, the duration of the violation is also crucial for the legality of a fine notice.
- Criterion 2: Fault
- It must be a blameworthy – that is, self-inflicted and not caused by
external circumstances – distance violation
- If there are no other events that reduce the distance, the driver can be expected to recognize and correct the distance violation within the aforementioned 3 seconds.
- It must be a blameworthy – that is, self-inflicted and not caused by
Penalties and Fines for Distance Violations
In general: The higher the speed and the shorter the distance, the higher the penalty. The exact amount of the fine is publicly available in the current penalty catalog or in Annex 1 to the Penalty Catalog Regulation, starting from item 12.
There are separate regulations for:
- Trucks > 3.5 tons
- Coaches
- Provisional drivers of cars
- Unnecessary braking and tailgating. These may be prosecuted as offenses under the Criminal Code (StGB).
Fines and Points for Car Drivers
It is obvious that the safety distance must be greater the faster the vehicles are traveling. Therefore, fines, points, and driving bans are determined based on both the speed driven and the measured distance.
The relevant speed intervals for distance violations are:
- Less than 80 km/h (differentiations: without endangerment, with endangerment, with property damage)
- 81 km/h to 100 km/h
- 101 km/h to 130 km/h
- More than 130 km/h
Within these intervals, fines are graded according to the measured distance. Below 80 km/h, flat fines are imposed; above 80 km/h, half the speedometer value in meters is set as the minimum distance (example: speed 120 km/h, minimum distance ⇒ half of 120 = 60 meters). Violations of the minimum distance are penalized in the following intervals:
- Less than 5/10 of the respective minimum distance (e.g., 120 km/h: between 48 and 59 m)
- Less than 4/10 of the minimum distance (e.g., 120 km/h: between 36 and 47 m)
- Less than 3/10 of the minimum distance (e.g., 120 km/h: between 24 and 35 m)
- Less than 2/10 of the minimum distance (e.g., 120 km/h: between 12 and 23 m)
- Less than 1/10 of the minimum distance (e.g., 120 km/h: between 1 and 11 m)
Special Regulations for Drivers of Trucks > 3.5 Tons and Coaches
Due to their mass, trucks and coaches have a longer stopping distance. Accidents caused by trucks on highways often result in personal injuries and are rightly feared. For this reason, different regulations apply to trucks regarding the minimum distance, and distance violations are severely penalized.
Minimum Distance for Trucks over 3.5 Tons and Coaches
Over 50 km/h, the minimum distance is: 50 meters to the vehicle in front, even during overtaking
Penalty:
- Failure to maintain the minimum distance of 50 m is punishable by a fine of €80 and one point in the Flensburg traffic violations register.
- For trucks carrying hazardous materials, the fine is €120, and one point is also entered in the driver fitness register.
Special Regulations for Provisional Car Drivers
Novice drivers during their provisional period are more likely to cause accidents. This is particularly true for accidents resulting from distance violations. Therefore, distance violations at speeds exceeding 80 km/h are considered serious offenses. This means:
The provisional period is extended by 2 years
Attendance at an advanced driver training course is mandatory; failure to attend will result in the revocation of the driver’s license
In combination with other offenses, an invitation to attend traffic psychological counseling may also be issued.
